

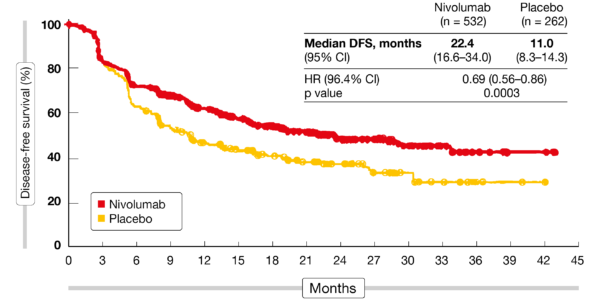
The benefit of nivolumab compared with placebo in patients with esophageal cancer or GEJ cancer was seen across all subgroups, including patients with squamous-cell carcinoma (HR, 0.61), adenocarcinoma (HR, 0.75), node-negative disease (HR, 0.74), and node-positive disease (HR, 0.67). “Although overall survival data are not mature, the doubling of median disease-free survival will almost certainly translate into an overall survival benefit,” Dr Ilson noted. Both distant and locoregional recurrence occurred less often with nivolumab than with placebo (29% and 12% vs 39% and 17%, respectively). RESULTS: Nivolumab significantly prolonged disease-free survival with a median of 22.4 months compared with a median of 11 months for placebo (hazard ratio, 0.69 96.4% confidence interval, 0.56-0.86 P <.001). The primary end point was disease-free survival. The maximum duration of the study intervention was 1 year. Patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to nivolumab or to placebo.
#Checkmate 577 trial#
METHODS: CheckMate-557 was a global, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial of 532 patients with resected stage II or III esophageal cancer or GEJ cancer who had received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and had residual pathologic disease. “CheckMate 577 is a practice-changing trial in the treatment of esophageal cancer,” Dr Ilson suggested. The study evaluated the use of the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab as adjuvant treatment after chemoradiotherapy and surgery for esophageal cancer or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer.
“Improvement in survival among patients with esophageal cancer has been long awaited in those undergoing the arduous journey of chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery,” Dr Ilson emphasized, while discussing the findings from the CheckMate-557 clinical trial, which were published in the same issue. Ilson, MD, PhD, discussed the benefits and limitations of current treatments for esophageal cancer, noting that the current debate is whether chemotherapy alone or chemoradiotherapy is the preferred strategy for esophageal cancer before surgery. Commenting on the recent publication of the CheckMate-557 study in an accompanying editorial published in the New England Journal of Medicine, David H. However, the risk for recurrence after this treatment remains high, especially among the majority of patients who do not have a pathologic complete response.

Chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery is the standard of care for patients with resectable, locally advanced esophageal cancer. Gastrointestinal Cancer Monthly MinutesīACKGROUND: Esophageal cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide.Advances in Dual Immunotherapy Cancer Treatments.These results represent the first treatment advance in many years for these patients, potentially establishing adjuvant nivolumab as a new standard of care. Data including DFS rate and an analysis of DFS across pre-specified subgroups will be presented.Īdjuvant nivolumab is the first therapeutic to provide a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in DFS vs placebo and a well-tolerated safety profile in patients with resected EC/GEJC, who have received neoadjuvant CRT. The frequency of serious TRAEs and TRAEs leading to discontinuation were ≤ 9% with nivolumab and 3% with placebo (Table). The majority of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were grade 1 or 2. At a pre-specified interim analysis, adjuvant nivolumab showed a statistically significant improvement in DFS vs placebo (HR 0.69 P = 0.0003) median DFS was doubled (22.4 vs 11.0 mo, respectively Table). Approximately 70% of patients had adenocarcinoma and almost 60% had a pathologic lymph node status ≥ypN1 in both groups. Indication : Esophageal Cancer, Gastroesophageal junction cancerħ94 patients were randomized (nivolumab, 532 placebo, 262).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
